Archive for the 'Australian Dollar' Category
Canadian Dollar Slated to Outperform Other Commodity Currencies
In the same vein as Monday’s and Tuesday’s posts (covering the New Zealand Dollar and Australian Dollar, respectively), I’d like to use today’s post to look at another commodity currency - the Canadian Dollar. The Loonie, it turns out, has also benefited from the a recovery in risk appetite and concomitant boom in commodity prices; it has appreciated by 7% against the USD in the last month alone, en route to a ten-month high. “All in all, with almost everything going its way these days (besides the crummy weather and the impact on tourism), a return trip to parity - last visited nearly one year ago - doesn’t seem far fetched,” chimes one optimistic analyst.
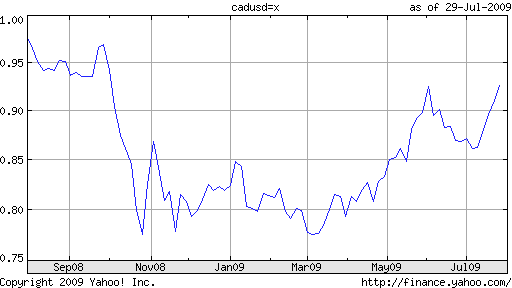
Like Australia and New Zealand, Canada’s economic fate is tied closely to commodity prices. Simply, as oil and other natural resources have inched closer to last year’s record highs, the Loonie has rebounded proportionately. “Raw materials account for more than 50 percent of Canada’s export revenue. Crude is the nation’s largest export.” Of course, this relationship works both ways. Any indication that the global economic recovery is stalling, and commodities prices would likely tumble, bringing commodity currencies down likewise.
Unlike the Australian Dollar and New Zealand Dollar, the Loonie has never really held much appeal as a carry trade currency. Even at their peak, Canadian interest rates were mediocre, from the standpoint of yield. The current rate is a measly .25%, compared to 2.5% in New Zealand and 3% in Australia. Moreover, while Australia may begin tightening as soon as the fall, “The Bank of Canada committed to keep its key policy rate at the lowest possible level until the spring of 2010,” after voting to hold rates at yesterday’s rate setting meeting. This interest differential could explain why the Aussie has outpaced the Loonie of late.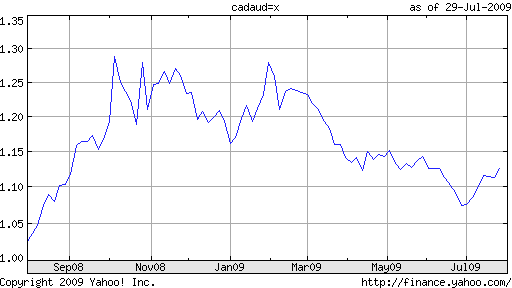
Another key difference - and potential explanation for the currencies’ recent divergence - is that Australia is considered part of the Asian economic zone, while Canada’s economic fortunes are closely aligned with those of its main trading partner, the US. China, alone, is helping to lift Australia out of recession. The US, meanwhile, is still struggling to find its feet. Hence, it is projected that Canadian GDP will contract by 2.3% in 2009, while Australian GDP may fall by a modest .5%. “When things look bad, you are more likely to sell Canada than the Australian dollar because its economy is moderated by Asian growth,” explains one analyst.
Going forward, this regional differentiation could actually work to the advantage of Canada, which is forecast to grow by an impressive 3% in 2010, compared to 1% growth in Australia. Accordingly, one analyst advises that “Investors should sell Australia’s dollar against Canada’s as a ‘relative commodity play’ because an attempt by China to reign in bank lending on concern it may be creating asset-price bubbles could slow Asian growth…’The Canadian dollar should outperform because it is much more closely linked to a recovery in the U.S.’ “

Reserve Bank of Australia Could be the First to Hike Rates
Based on the chart below, which plots the Australian Dollar against the New Zealand Dollar over the last two years, one might be tempted to conclude that the two currencies are identical for all intents and purposes. Rather than suffer the inconvenience of separately analyzing the Australian Dollar, why not just read yesterday’s post on the New Zealand Dollar, and leave it at that?
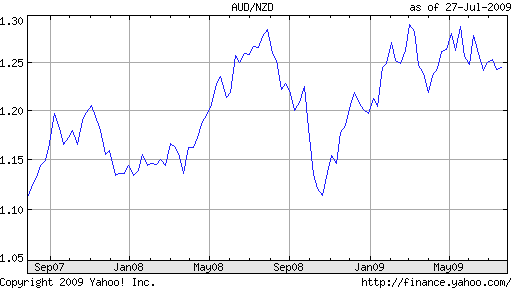
But this chart belies the fact that while the two currencies, have risen and fallen (in near lockstep) in sync with the ebb and flow of risk aversion, this could soon change. While the near-term prospects for the New Zealand economy are dubious, sentiment towards the Australian economy is more consistently optimistic. “Central bank Governor Glenn Stevens said the nation’s economic downturn may not be ‘one of the more serious’ of the post-World War II era.” In addition, “Stevens said the nation’s economy may rebound faster than the central bank had predicted six months ago on improving confidence among consumers and businesses alike.” The latest projections are for a fall in .5% contraction in GDP in 2009 followed by a 1% rise in 2010.
Meanwhile, government spending is surging: “The Australian government forecast its largest budget deficit on record of A$57.6 billion for fiscal year 2009-10, or 4.9% of GDP.” Combined with the steady recovery in commodity prices and the resumption of residential construction, this could soon trickle down through the Australian economy in the form of inflation. It’s no wonder, then, that the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) could begin tightening interest rates as early as December, in order to mitigate against the possibility of inflation in 2011 and 2012.
In fact, Governor Glen Stevens has been raising eyebrows with his unequivocal comments about raising rates. “I’ve never seen written down … I’ve never heard in discussion in the institution, some rule of thumb that says we wait until unemployment’s peaked before we lift the cash rate…I think it depends what else is happening, and also depends how low you went. We eased very aggressively,” he said recently. As a result, traders are betting that rates will be 1.13% higher one year from now than they are today.
This development should be of especial interest to forex traders. Australian interest rates are already the highest in the industrialized world. When you consider “the market’s expectations that the RBA is likely to be the G-10 central bank which is likely to hike first,” it goes a long way towards explaining the 18% rise in the Aussie that has taken place in 2009 alone. Compare a hypothetical 4% RBA benchmark rate to the .1% in Japan and ~0% in the US, and carry traders will start to salivate.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home